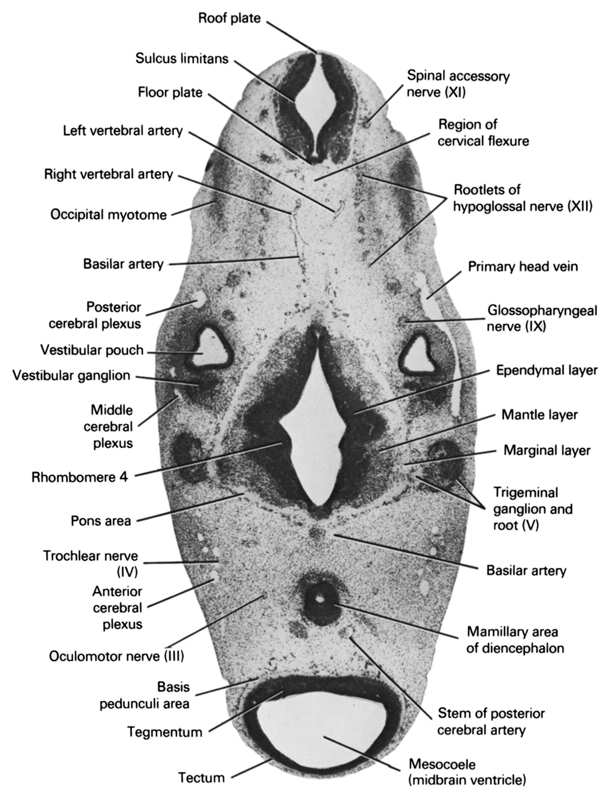
A section through the region of the cervical flexure, trigeminal nerve root and mamillary area of the diencephalon.
Observe:
1. The cranial edge of the occipital myotomes.
2. The anterior, middle and posterior cerebral plexuses, which drain into the primary head vein.
3. The vertebral arteries about to join to form the basilar artery which is continuous with the posterior cerebral artery.
4. The vestibular ganglion of the vestibulocochlear nerve adjacent to the vestibular pouch.
5. The trigeminal ganglion adjacent to the pons area of the metencephalon.
Keywords: anterior cerebral plexus, basilar artery, basis pedunculi area, ependymal layer, floor plate, glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), left vertebral artery, mamillary area of diencephalon, mantle layer, marginal layer, mesocoele (midbrain ventricle), middle cerebral plexus, occipital myotome, oculomotor nerve (CN III), pons area, posterior cerebral plexus, primary head vein, region of cervical flexure, rhombomere 4, right vertebral artery, roof plate, root of hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), spinal accessory nerve (CN XI), stem of posterior cerebral artery, sulcus limitans, tectum, tegmentum, trigeminal ganglion and root (CN V), trochlear nerve (CN IV), vestibular ganglion, vestibular pouch
Source: Atlas of Human Embryos.
