Prenatal Form and Function – The Making of an Earth Suit
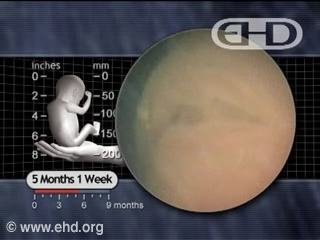
Unit 14: 4 to 5 Months (16 to 20 Weeks)
 Closer Look:
Closer Look:
 Applying the Science:
Applying the Science:
Copyright © 2006 EHD, Inc. All rights reserved.

In the eye, the retina now has discrete layers.1 The vast majority of neuron multiplication in the brain is complete by 16 weeks.2 In the teeth, enamel begins to develop between 16 and 20 weeks.3 Beginning at 18 weeks, ultrasound scans show a distinct type of motion in the fetal voice box, or larynx (lar’ingks), similar to movements made during speaking.4
From 18 to 20 weeks, fetal movement, breathing activity, and heart rate begin to follow daily cycles called circadian (ser-ka’de-an) rhythms;5 the same rhythms that characterize various biological activities throughout life.


In later pregnancy, the womb becomes a relatively noisy place. When doctors put a stethoscope on the belly of a pregnant woman, they need an experienced ear to make sense of the many noises inside. Two heartbeats, one belonging to the mother and the other to her fetus, beat at different rates, creating competing muffled pulsating noises. A soft blowing sound comes from the woman's womb as blood fills the vessels of her uterus. In 15% of pregnancies, blood rushing through the umbilical cord creates a whistling sound that keeps in time with the fetal heartbeat. Also, gas gurgles in the woman's intestines. Finally, each time the fetus moves around in the uterus, the motions add to the noise.

For the fetus, this racket is very familiar and even comforting. Considering all of this noise, the old suggestion of an alarm clock in the crib to soothe the baby just might work after all.
Listen closely;
what do you hear?
1 F. Gary Cunningham, Paul C. MacDonald, Norman F. Grant, et al., Williams Obstetrics, 20th ed. (Stamford: Appleton and Lange, 1997), 30.
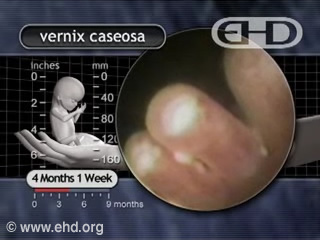
A protective white substance, called vernix caseosa (ver’niks caseo’sa), now encases the fetus,6 protecting the skin from exposure to amniotic fluid.7
By about 19 weeks, the number of oogonia within the ovaries of a female fetus peaks at approximately 7 million. From this point, not only does oogonia production end forever, but their numbers decrease to about 2 million by birth. These oogonia give rise to several thousand primary oocytes.8

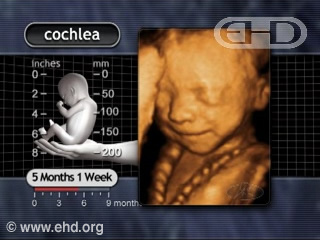
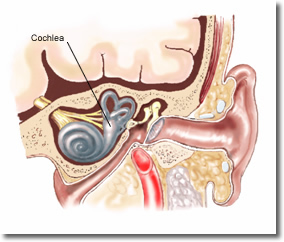
The cochlea is the frequency analyzer of the ear and converts sound waves of varying frequencies into electrical impulses which are then communicated to the brain. By 20 weeks it reaches adult size9 within the fully developed inner ear.10
From now on, the fetus will respond to a growing medley of sounds.11
Copyright © 2002 Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. All rights reserved.
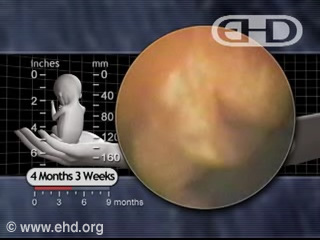
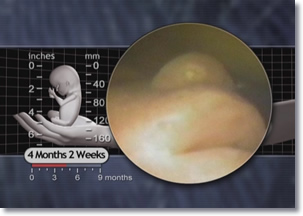
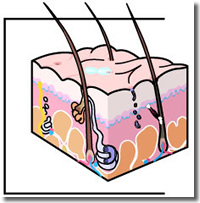
With the eyebrows nearly complete,12 hair now begins to grow on the scalp.13 All skin layers and structures are present, including hair follicles and glands.14
Copyright © 2002 Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. All rights reserved.
| 1 | Pringle, 1988. 179. |
| 2 | Dobbing and Sands, 1973. 766. |
| 3 | Pringle, 1988. 179. |
| 4 | Lopez Ramon y Cajal, 1996. 65. |
| 5 | de Vries et al., 1987. 333; Goodlin and Lowe, 1974. 349; Okai et al., 1992. 391, 396; Romanini and Rizzo, 1995. 121; Rosenwasser, 2001. 127; Vitaterna et al., 2001. 92. |
| 6 | Moore et al., 2000. 52. |
| 7 | Campbell, 2004. 48; Moore and Persaud, 2003. 107; O'Rahilly and Müller, 2001. 168. |
| 8 | Blackburn, 2003. 7; O'Rahilly and Müller, 2001. 25. |
| 9 | Lecanuet and Schaal, 1996. 5-6; Querleu et al., 1989. 410. |
| 10 | Valman and Pearson, 1980. 233-234. |
| 11 | Glover and Fisk, 1999. 882; Hepper and Shahidullah, 1994. F81; Querleu et al., 1989. 410; Sorokin and Dierker, 1982. 725, 730; Valman and Pearson, 1980. 233-234. |
| 12 | England, 1983. 25. |
| 13 | Moore and Persaud, 2003. 107. |
| 14 | Pringle, 1988. 180. |